
Research Projects
-

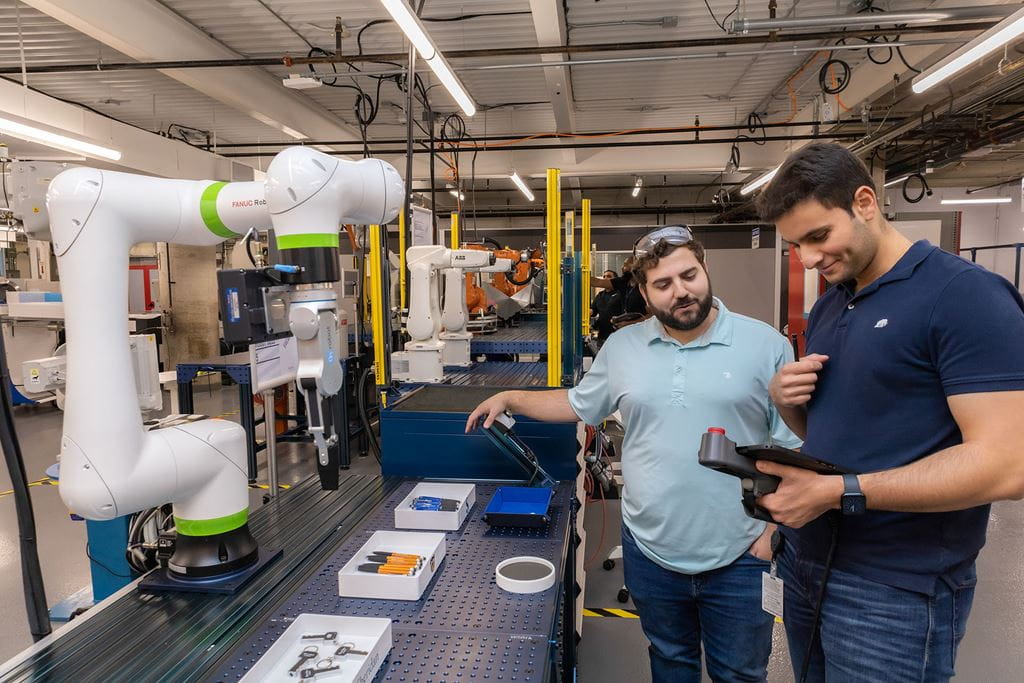
Automated Robotic Assembly and Testing of Fire Prevention Controllers
November 2025
CIM has collaborated with Mircom Group—global designer, manufacturer and distributer of intelligent building solutions—to address key challenges in the automated assembly and testing of fire prevention devices for building occupant safety.


Funding Agency/Program: FedDev Ontario / SONAMI
Industry Partner: Mircom Group
Principle Investigator: Ethan Shen
Co-Investigator: Mohamed Kasim
Student Research Assistants: Meetkumar Taylor, Ted Nguyen
Technology Areas: Manufacturing, machinery, electronic products
The primary goal of this research project was to develop an automated system for the assembly and testing of Mircom’s fire prevention module, with the goal of enhancing and expanding production of this key product. The project included consultation with robotics manufacturers and trialing of suitable robotics equipment for custom automation.
The Challenge: To modernize the existing assembly process that was time-consuming and labour-intensive, limiting production speed and scalability. Mircom partnered with CIM to transition to a fully automated solution that included unpacking, assembly, testing, engraving and packing. In the first phase of the project, the focus was on automating the assembly and testing stages, with preliminary exploration into the engraving process.
The Solution: The CIM research team worked on the design and development of an automated setup that can feed and accurately place key components such as the cover, base module, LED diffuser and PCB. The automated system developed using an ABB robotic setup demonstrated the ability to reliably handle parts, precisely assemble components, and efficiently conduct testing required to meet production quality standards. The project not only streamlined the current assembly process but also laid the groundwork for future integration of a fully automated production cell.
-

Process Demonstration for the fabrication of novel energy-efficient window framing
August 2025
CIM has collaborated with Vision Coatings Limited, a leading provider of finishing services for the fenestration industry in North America, including painting and lamination of profiles used in doors and windows. This partnership addressed production challenges in the scalable fabrication of alternative heat‑resistant material within the cavities of mass‑produced vinyl window framing.


Funding Agency/Program: NRC IRAP
Industry Partner: Vision Coatings Limited
Principle Investigator: Ethan Shen
Co-Investigator: Mohamed Kasim
Student Research Assistants: Stavro Gentile, Meetkumar Taylor, Ted Nguyen
Technology Areas: Automation, Elector-Mechanical Design
The project aim was to develop a method for the automated insertion of low-emissivity insulation into vinyl extrusion profiles to enhance thermal resistance properties, with the intent to replace traditional foam filling. A successfully demonstrated automated process would enable Vision Coatings to address a production bottleneck for a new window framing product that was limiting its growth and its ability to lead in modern energy efficiency standards.
The Challenge: The manual process of inserting heat-resistant aluminum foam insulation was slow, labour-intensive and prone to inconsistency. This process not only limited throughput but also presented challenges in quality control and operator safety, making it difficult to achieve the superior thermal performance required for certifications like Energy Star. Traditional foam-filling methods were not a viable alternative due to issues with flammability, moisture sensitivity and heat-induced deformation.
The Solution: To develop a scalable process with consistent insulation placement, a prototype of a mobile insulation insertion machine was designed that transforms the entire process. The final prototype features a mechanism that automatically pulls insulation through frame cavities up to 21 feet long. Key innovations overcome critical friction and material handling challenges and the system is equipped with integrated sensors and dual operator control panels, creating a safe, efficient and highly repeatable workflow with minimal manual intervention. Through this project, Vision Coatings is able to scale major production, significantly increase throughput while ensuring consistent high-quality output and enhance workplace safety. The impact of this project is transformative for improving the thermal performance of vinyl window frames, to ultimately reduce home energy waste.
-

Robotic Gait Simulator for Prosthetic Fitting
March 2024
ProsFit Care Inc. is a global assistive device provider collaborating with Sheridan’s Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing (CIM) on their Robotic Gait Simulator (RGS) project. This initiative, part of ProsFit’s Digital Double development program, aims to enhance prosthetic services through remote assessment and mobility optimization, leveraging an Integrated Digital Twin approach. This partnership is set to advance capabilities in predictive gait analysis, game-ified training, and health monitoring for prosthetic limb wearers.


Funding Agency/Program: FedDev Ontario/ SONAMI
Industry Partner: Prosfit Care Inc.
Principle Investigator: Nadim Arafa (MEET) and Joaquin Moran (MEET)
Student Research Assistants: Mohamed Kasim (MEET), Ted Nguyen (MEET)
Technology Areas: Mechanical Engineering, Robotics, Biomedical Engineering, Health Sciences
The aim of this phase of the RGS project is to build the data necessary to help improve prosthesis comfort for persons with one or more lower-limb amputation. The targeted outcome is to support professionals in the provisioning of prosthetic products and services to persons with amputation, to enable higher retention and success rates. Corrective prosthetic alignment targets include improving mobility by reducing tissue damage due to force dynamics, and pressure and strain/friction between the prosthesis and limb. Leveraging AI and scarce clinical resources will enable local intervention and direct amputee user interaction.
The Challenge:
Nearly half of lower-limb prosthetics end up being abandoned by amputees, largely due to discomfort and sores caused by inadequate fittings. In order to identify pressure points of discomfort or blistering, human gait movement patterns robotically rendered were to be applied to a prosthetic setup. Robotic simulation of the human gait required application of force and contact with a surface and appropriate experimental protocols to gather and classify information, as tests of this kind have not been performed before.
The Solution: The fabrication of a device to simulate a human limb with an attached prosthetic was successfully completed. An industrial robot and programming support was provided through a partnership with ABB Canada was used to simulate a human gait and allow measurements of force, pressure, and stress on the device. The six-axis industrial robot that mimics human gait movement patterns may now be used to identify pressure points of discomfort or blistering. Those results are then fed back to the digital twin platform with a finite element model to refine parameters, ultimately enabling better outcomes in the prosthetic manufacturing and fitting process.
-

Motion tracking for High Performance Sports
March 2024
Deepthought AI Consulting, located in Milton, ON, specializes in delivering analytics and AI solutions to clients within the sports industry. Their projects encompass a wide range of solutions, including motion tracking, scoring, and score analytics. Deepthought AI is collaborating with Sheridan’s Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing (CIM) to demonstrate motion capture and data analysis to optimize sports performance.


Funding Agency/Program: FedDev Ontario/ SONAMI
Industry Partner: Deepthought AI Consulting Inc.
Principle Investigator: Ameera Al-Karkhi(MEET), Asama Nseaf (MEET)
Co-Principle Investigator: Ethan Shen (MEET)
Student Research Assistants: Hassan Saleem (MEET), Yash Rathod (MEET)
Technology Areas: Computer vision, software algorithm, motion tracking, stereo vision
This motion capture for high performance sports project aims to develop a body tracking system using video data captured by Microsoft Kinect Camera. The generated body tracking data will serve as a tool for certified physiotherapists and sports exercise consultants, facilitating in-depth physiotherapy analysis with the goal of enabling improvement of sports-focused tasks. This technology employed enables precise tracking and assessment of body movements, supporting therapeutic interventions and exercise planning by medical professional for athletes. The project seeks to bridge the gap between technology and healthcare, offering an innovative solution for enhancing patient care and improving sports performance.
The Challenge:
The project aim was to create a human tracking system for physiotherapists and sports consultants using data from Microsoft Kinect cameras. It was a specific focus to carefully track how the body moves, to required detail to enable improving recovery and maximizing sports performance.
The Solution: The project has successfully used video data from the Microsoft Kinect Camera to build a human tracking system. With the help of this system, certified physiotherapists and sports exercise advisors can analyze sessions in-depth and assess and track patients' progress more precisely. The project's integration of technology with healthcare input is a differentiator to improve patient care and maximize sports performance, by improving the effectiveness of rehabilitation and enabling customization of exercises.
-

Creation of a Robotic Imaging System with AI for Inspection
December 2023
A. Berger Precision is a leading manufacturer specializing in the production of high precision metal parts, specifically tailored for automotive engines. They play a crucial role in the automotive industry, providing top-quality metal parts that contribute to the reliable and optimal performance of engines.


Funding Agency/Program: FedDev Ontario/ SONAMI
Industry Partner: A. Berger Precision
Principle Investigator: Ethan Shen, CIM
Co-Principal Investigator: Ameera Al-Karkhi, MEET
Student Research Assistants: Stavro Gentile (MEET), Sameer Ahmed (MEET), Yash Rathod (ACS), Dhruvkumar Sojitra (ACS)
Technology Areas: Robotics, Automation, Vision Systems, Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence
In collaboration with Sheridan’s Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing (CIM), A. Berger Precision aimed to demonstrate an automated inspection system which improves upon the current manual inspection system, enhancing accuracy in cases when 100% visual inspection is required. The ambitious final goal for an automated inspection system is that all visual defects should be detected on the outer and interior surfaces of parts.
The Challenge:
- Develop an advanced automated inspection system that surpasses the existing manual inspection process in accuracy and efficiency.
- Design and demonstrate an imaging system capable of capturing high-resolution images of parts, specifically with the ability to detect 50um size defects.
- Implement and train an artificial intelligence model to achieve a remarkable 95% success rate in detecting visual defects, effectively distinguishing variations between flawless parts and even minor imperfections.
The Solution: The project established a proof-of-concept automated inspection system and involved the development of a functional robotic imaging and inspection system, accompanied by the creation of an AI model specialized in detecting defects on targeted components. This initial phase focused on showcasing the proficiency of the imaging system and AI model in identifying exterior defects. To achieve this, an automated imaging system comprising a digital camera and ABB robot was integrated for image acquisition. Simultaneously, an AI algorithm was implemented and trained to effectively detect defects on the inspected parts. This integrated approach demonstrated enhanced efficiency and accuracy in defect detection for Berger high-precision components.
-
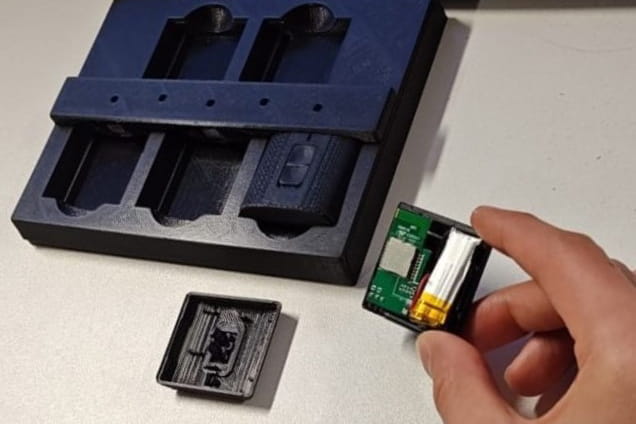
Design and Manufacturability Study of Sensor Enclosures for Rehab Tracking
December 2023
LEVEL Motion is a medical technology company developing a sensor system to track movement during rehabilitation to enhance exercise compliance, clinical decisions, and processes. The LEVEL system consists of wearable sensors, paired with remarkable software, that allows for clinicians to observe and measure movements performed during and after rehabilitation.


Funding Agency/Program: FedDev Ontario/ SONAMI
Industry Partner: LEVEL Motion
Principle Investigator: Victor Bravo, MEET
Co-Principal Investigator: Ethan Shen, CIM
Student Research Assistants: Theodore Nguyen, MEET
Technology Areas: 3D Printing, Design for Manufacturing, Biocompatible Materials, Medical Devices, Wearable Sensing
The objective of this project was the development and optimization of sensor and charger enclosures originally created by LEVEL Motion, by following the design for manufacturing (DFM) process. The LEVEL wearable sensor system precisely measures joint range of motion and speed of motion during rehabilitation activities. As the sensor enclosure is to be used for rehabilitation purposes, it must be biocompatible and resistant to impact energy caused by drops at certain heights. A cost analysis was desired with a comparison between different materials produced using various 3D printing techniques such as FDM, SLS and Polyjet printing.
The Challenge: In addition to manufacturability, biocompatibility and durability, a main design concern regarding the product was a charging issue between the sensor and charging enclosure. Due to dimensional miss-match between parts, pins between entities were not aligning properly and was causing the charge to occasionally stop or inhibit charge.
The Solution: 3D Printed prototypes were produced with the specifications provided by LEVEL to assess the manufacturing parameters and test adjustments to correct the fitting of sensor enclosures in the charging station, improve impact strength, surface quality and ease of manufacturing. As milestones were being accomplished during the execution of the project, new manufacturing challenges arose which were incorporated into the objectives of the project. The inspection of the prototypes produced at CIM revealed the cause of the charging problem, which was the printing process resulting in a misalignment between the PCB connectors and the sensor enclosure. A modification in the part fabrication process produced an improvement in the strength of the clips. Comparison of different biocompatible materials and selection was accomplished. As part of the DMF study, research performed on the injection molding alternative produced preliminary results about the determination of design features that require adjustment.
-

Technical and Economic Feasibility of Combined Heat and Power for Electroplating Process
March 2023
The Dovercourt Group is one of the leading groups of metal finishing companies in North America and provides plating services to commercial and automotive part suppliers. This research project investigated the feasibility of reducing power requirements in electroplating through the use of Combined Heat and Power (CHP).


Funding Agency/Program: NRC IRAP/CTO
Industry Partner: Dovercourt Management Corp.
Principle Investigator: Dr. Amin Ghobeity, MEET
Co-Investigator: Dr. Seyedfoad Aghamiri, MEET
Student Research Assistants: Damon Soni, Gia Ngo, MEET
Technology Areas: Electroplating, Manufacturing, Energy Systems, Thermal Modeling
Electroplating is an important process in parts manufacturing, critical to finishing functional parts such as automotive components. During the electroplating process, thermal and power consumption are high and energy system optimization approaches could significantly reduce the cost and combined energy draw.
The Challenge: To conduct a feasibility study modeling the impact of the use of CHP (Combined Heat and Power) units producing thermal energy and electricity simultaneously from a single energy source, and recovering heat to boost efficiency.
The Solution: Thermo-economic feasibility of CHP for electroplating was completed. Benchmarking of existing electrical and thermal power requirements were used as the input model for the design input for sizing and optimization of the CHP unit. Economic analysis considering electricity and natural gas prices was also conducted. Recommendations of CHP units with the greatest positive impact were provided to the industry partner.
-

Analysis of Remote Monitoring Thermal/Visual Data at Electric Power Stations
March 2023
Systems with Intelligence is a Mississauga company providing next generation utility grade, touchless monitoring solutions for critical assets increasing reliability, safety and reducing O&M costs for companies worldwide. This research project investigated the improvement of automated methods for detecting hot spots which may occur at electrical power stations.


Funding Agency/Program: NRC IRAP/CTO
Industry Partner: Systems with Intelligence Inc.
Principle Investigator: Ammar Al-Qaraghuli, MEET
Co-Investigator: Asama Nseaf, MEET
Student Research Assistants: Yash Rathod, Dhruvkumar Sojitra, MEET
Technology Areas: Remote Monitoring, IOT, Vision Systems, Data Analytics, Machine Learning
Electrical power stations require constant monitoring, and the detection and analysis of hot spots are critical due to the possibility of these leading to a catastrophic event such as a critical equipment failure or fire. Automated detection and machine learning models were developed and tested for hot spot detection.
The Challenge: To demonstrate machine learning models based on computer vision and analytics systems, which would be suitable for system deployment, testing, and performance tuning.
The Solution: Deep learning-based architectures and a machine learning system were built for two tasks: fire detection and gauge reading in electric power stations. From research datasets, the algorithms were built and tested using public scientific datasets for fire detection and augmented images dataset for gauge detection. Performance evaluation of the demonstrated systems attained accuracy rates in the range of 97.5% with the opportunity for improvement upon further development.
-

Optimize Design and Commissioning of a Horizontal SAM unit to Dealcoholize Beverages
December 2022
Drystill is a Mississauga company possessing chemical separation process technology particularly suitable for temperature-sensitive materials and resulting in reduced energy and water consumption. For this demonstration project, the SAM unit was designed, fabricated and assembled on site using multiple manufacturing processes including 3D printing. Separate solutions of dyed water were circulated separately via two manifolds operated under vacuum and room temperature, observing flow and pressure measurements.

.png?h=37&w=120&rev=f6f5a3aaaf0a4d4992579e600d041d8c&hash=39A8B7BFF62E229FDC3235D2244E8834)
Funding Agency/Program: FedDev Ontario/ SONAMI
Industry Partner: Drystill Holdings Inc
Principle Investigator: Manju Sunil Varghese, CHEM
Co-Investigator: Dr. Ethan Shen, Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing
Student Research Assistants: Harmanjot Singh (MEET), Akashdeep Singh (MEET)
Technology Areas: Separation Chemistry, Chemical Engineering, Mechanical Assembly, Prototyping
Design, create and assemble the equipment required to make a working prototype of a horizontal SAM (Stripper-Absorption Module), to work under low temperature, vacuum conditions ideal for a gentle dealcoholization of beverages, to retain the subtle flavors and aromas of beer and wine.
The Challenge: To design the equipment and select the required material for the prototype (SAM), assemble while ensuring adequate sealing, and test under vacuum.
The Solution: Two manifolds were connected with pipes pass separate solutions at top and the bottom of the main shell, and a geometrical design was implemented to enable the fluids to circulate easily without restrictions. The manifolds were custom designed, and drilling and shaping were constructed manually using a custom-made rig by team members. The system was optimized for operation of the SAM unit to maintain constant vacuum at 30 torr for at least one hour. Vacuum leaks were determined at the pipe joints to iteratively improve the required seal although further work is required to ensure internal sealing of the unit. Flow distribution over the heat pipes was improved by designing a flow distributor.
-

Cloud Based Condition Monitoring
October 2022
Sarox Technology Inc. is a Canadian engineering firm with experience in design, development, manufacturing and testing of electronic devices in multiple industries. Power outage in machinery systems is one of the main concerns of multiple industries. Sarox platforms continuously monitor, analyze and assess machinery health to avoid unplanned outages.


Funding Agency/Program: NSERC/ Engage
Industry Partner: Sarox Technology Inc.
Principle Investigator: Dr. Daryoush Mortazavi, MEET
Student Research Assistant: Alireza Bidkhori, MEET
Technology Areas: Information Systems and Technology, Cloud Computing, Preventive Maintenance, Electrical Machinery
Currently, Sarox provides predictive maintenance planning for many industries, conducted via collecting electrical machinery parameters and monitoring using wired sensors and a local PC. Development of remote monitoring of machinery parameters and analysis using an AI algorithm enables the possibility of more effective prediction of maintenance intervals.
The Challenge: Cost-effective, smart electrical machinery malfunction detection and maintenance prediction is required to reduce the maintenance costs through predicting and/or preventing maintenance periods of electrical equipment, especially motors and generators in manufacturing industries.
The Solution: Condition monitoring is one method to prevent outage costs via monitoring parameters of electrical machines on power lines, stators or rotors, such as voltage, current, temperature and vibration. This project utilized Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) based solutions that collect data from industrial sensors with machine-to-machine communications and automation technologies to monitor health conditions of electrical machines and predict maintenance period. This project utilized Python code and data received in RaspberryPi using serial TTY connection from an electric motor, and a GUI was created so that test parameters can be easily monitored and trigger alarms for preventive maintenance procedures.
-

Power Quality Measurement IOT Device
September 2022
Arshon Silicon Technology Inc. is an Ontario-based engineering firm with expertise in the design and manufacturing of electronic boards. Arshon offers engineering services and applied solutions for enterprises in the industrial and commercial sectors, and has developed and produced products monitoring and logging critical parameters in the power industry for 10 years.


Funding Agency/Program: NSERC/ Engage
Industry Partner: Arshon Silicon Technology Inc.
Principle Investigator: Dr. Daryoush Mortazavi, MEET
Student Research Assistants: Stephan Vorster, Jasprit Snght, MEET
Technology Areas: Information Systems and Technology, Cloud Computing, IOT, Preventive Maintenance, Power Distribution
Power outages in power distribution systems are one of the main concerns of the power industry. Therefore, developing solutions that can predict the maintenance periods and prevent unwanted maintenance is crucial in decreasing outage costs and improving system reliability.
The Challenge: Cost-effective, smart electrical machinery malfunction detection and maintenance prediction is required to reduce the maintenance costs through predicting and/or preventing maintenance periods of electrical equipment, especially motors and generators in manufacturing industries.
The Solution: The collaborative team researched, tested and explored multiple cross-platform frameworks for developing, implementing and testing an IoT and mobile solution to measure power quality. The project resulted in an enhanced mobile UI/UX for engagement, AI readiness activities, and a new channel of user data analytics. The team implemented LoRa communication to transfer data from PIC microcontroller to a Lora receiver. In addition to power line information, the location of the installed device was extracted using a GPS module and sent over the LoRa module. A metering IC chip was used to get power line data like RMS, Peak, and harmony values.
-

Automation for Flagpoles
September 2022
HCI Lighting is a manufacturer of industrial commercial light fixtures. Their original business was in interior lights but they have focused for the past several years on industrial and commercial sectors. This applied research project explored the use of 3D materials for their industrial fixtures, as well as the demonstration of integrated prototypes for their new product lines.


Funding Agency/Program: FedDev Ontario/ SONAMI
Industry Partner: HCI Lighting
Principle Investigator: Dr. Ethan Shen, Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing
Student Research Assistants: Stavro Gentile (MEET), Darius Innis (MEET)
Technology Areas: 3D Printing, IoT, Mechanical Systems, Automation
Raising and lowering flags at locations that are not easy to reach is time consuming and labour intensive. With IoT technology becoming readily available, most flagpole operations could be carried out automatically. HCI lighting is investigating the incorporation of automation capability into flagpoles to enable remote flag motion control.
The Challenge: Designing a combination of motor/pulley system and the integration of a micro-controller to communicate with user interface app on a mobile phone for remote control.
The Solution: The integrated system prototype was designed based on appropriate components for the application, iterative design, and feasible use in industry. A motor was chosen based on load, and 3D printed pulleys were custom designed to improve gripping on the rope. Bluetooth technology was used as the communication protocol between mobile phones and the micro-controller. The prototype successfully fulfilled the industry partner requirements, and the technology was transferred to the industry partner.
-

Numerical Simulation of Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in CANDU-Reactor Fuel Channels
June 2022
Stern Laboratories Inc. is a Canadian owned private corporation that conducts reliability and safety experiments for utilities, nuclear reactor, and fuel vendors. They embarked on a research project with the Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing (formerly known as the Centre for Advanced Manufacturing and Design Technologies) team to explore the flow field and heat transfer characteristics of coolant flow inside a fuel channel in a CANDU reactor.


Funding Agency/Program: FedDev Ontario/ SONAMI
Industry Partner: Stern Laboratories Inc
Principle Investigator: Joaquin Moran, MEET
Technology Areas: Mechanical Engineering, Fluid Mechanics, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), Nuclear Power
Modeling the flow field around the fuel bundle is essential for predicting the surface temperature of the radioactive fuel and has important safety and optimization implications. Our goal is to utilize Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) to predict the flow parameters and compare with existing experimental measurements. The outcome of the research project will allow to develop safer reactors and is aligned with Ontario’s clean energy policies and objectives.
The Challenge: Obtain an acceptable model to replicate experimental measurements of temperature in a CANDU fuel element.
The Solution: Numerical Simulation and High-Performance Computing were successfully used to study the effect of different mesh densities and turbulence models in the solution of this problem. The final approach, which included a complex 3D mesh and used RSM for modelling of flow turbulence, could reproduce the temperature profiles obtained in practical experiments.
-

Design and Manufacturing of POP-Q+ Measurement Tool
May 2022
Cosm is developing Gynethotics™, the world's first custom-made gynecological prosthetic for female pelvic floor disorders. This applied research project explored the design and manufacturing of a mechanical measurement tool to obtain more accurate dimensions from female pelvic clinical exams.


Funding Agency/Program: FedDev Ontario/ SONAMI
Industry Partner: COSM Medical
Principle Investigator: Dr. John Phillips, Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing
Technology Areas: 3D Printing, Design, Biomedical Engineering, Women's Health
The current Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantifications System (POP-Q) is quantified by using finger measurements, which suffers from subjectivity and inconsistency amongst clinicians. It was hypothesized that using a mechanical measurement tool will increase accuracy and repeatability of clinicians recording POP-Q alongside other assessments associated with pessary fittings.
The Challenge: There were currently no medical instruments available that can measure the parameters related to pessary fittings and Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantifications System (POP-Q). The tool needed to be single use, relatively inexpensive, biocompatible, ergonomic, and able to accommodate the anatomical constraints of the human vaginal canal.
The Solution: Multiple mechanical tools were designed, and prototypes were developed that could measure key parameters of pelvic floor and vaginal assessment including the POP-Q. The tools were evaluated by bench testing and clinician feedback. 3D printing was extensively explored as a manufacturing strategy to produce both the prototypes and the short run of tools for clinical testing. Different 3D printers and materials were explored to evaluate the biocompatible, durability, and functionality. One of the designs was refined through multiple iterations and was developed to meet the need of the company to explore clinical trials.
-

Harvester Robotic System
March 2022
Acrebot Inc. has been created in response to last year's COVID-related hardships experienced by Ontario farmers. The company is working on developing an autonomous robotic greenhouse produce harvester that, at some point, would be able to close the gap in greenhouse labour requirements.

Funding Agency/Program: FedDev Ontario/ SONAMI
Industry Partner: Acrebot Inc.
Principle Investigator: Ramzy Ganady, Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing
Student Research Assistants: Mohamed Kasim (MEET), Darius Inniss (MEET), Yashkumar Rajeshbhai Patel (MEET)
Technology Areas: Robotics, Vision, Mechanical design, and programming
Many Canadian farmers are experiencing long-term, structural labour shortages, and are unable to meet the workforce needs of greenhouse harvesting. To reduce labour shortages, a machine may take on the more autonomous harvesting tasks on farms. This project aimed to develop an autonomous robotic greenhouse harvester that would eventually close the gap in greenhouse labour requirements.
The Challenge: To develop a vision-guided robot, capable of identifying and harvesting tomatoes, bell peppers and cucumbers — vegetables that make up the largest share of greenhouse vegetables grown in Canada.
The Solution: The Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing and Acrebot Inc. worked collaboratively on an eight month project to develop a prototype for the new system. Acrebot had already developed a vision system for the robot to recognize the vegetables, and by working with the Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing, the vision system was physically demonstrated with industrial robots. The Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing team helped establish communication between the vision and robotic systems, and then iterated and prototyped Acrebot's design for the robotic arm's end effector that would be able to grab the vegetables and cut off their stems, and then deposit them into collection boxes. The system successfully demonstrated the harvesting of the target vegetables and is a positive example of the benefits of de-risking a business's investment in new technology.
-

3D metal printing design for enhanced cooling in blow moulding
December 2021
Compact Mould Ltd. is an innovative Canadian-based manufacturer of high-quality Extrusion Blow Moulds, Stretch Blow Moulds, and Injection Stretch Blow Moulds. In partnership with the Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing (formerly known as the Centre for Advanced Manufacturing and Design Technologies), Compact Mould explored 3D design and fabrication enabled by metal 3D printing as a means to reduce cooling time and reduce cycle time.


Funding Agency/Program: FedDev Ontario/ SONAMI
Industry Partner: Compact Mould Ltd.
Principle Investigator: Dr. John Phillips, Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing
Student Research Assistants: Drew Pitchford (MEET)
Technology Areas: Metal 3D printing, Metal mold cooling
A key challenge in the manufacturing of parts via blow moulding is the cooling time required; cooling typically makes up 80 to 85 percent of the overall cycle time. Proper cooling time is not only a major factor in the end quality of a part — it's the most time consuming component of a molding cycle.
The Challenge: Molds and blow pins are typically manufactured using CNC machines and are therefore limited to designs that are achievable with subtractive manufacturing processes.
The Solution: Three different blow molding components with custom cooling strategies were designed and manufactured using Selective Laser Melting (SLM) 3D metal printing technology. The designs were analyzed and optimized before manufacturing using CFD thermal modeling and compared to traditional conventionally machined cooling strategies. The parts were made using 316L stainless steel which is suboptimal for mold tooling and cooling but were successfully tested. The 3D metal printed parts were shown to decrease molding cycle times when compared to the conventionally machined parts.
-
Simplified Authentication
September 2021
Simplified Automation (SA) is a SaaS product company that helps manufacturing companies digitize their internal lean focused workflows with a product called PET – Process Excellence Template. SA has been capturing and managing manufacturing-related data for multinational companies like Unilever and Whirlpool. With increasing complexity in the software and multiple applications within PET, SA required expertise and experience for relevance and compliance with industry standard for data security.


Funding Agency/Program: FedDev Ontario/ SONAMI
Industry Partner: Simplified Automation Inc.
Principle Investigator: Nicholas Johnston (Applied Computing, FAST)
Student Research Assistants: Imaan Kamau-Wanjiru (ACOMP), Omar Kooliyat (ACOMP)
Technology Areas: Cybersecurity, Authentication, Software Security Controls
This project reviewed the current login flow in detail so the existing security controls can be documented and assessed. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) for login was later introduced to support users without email addresses. Secure password and other MFA credential resets were also enabled.
The Challenge: Missing or outdated security controls of the web application login and password reset workflow results in vulnerability to attack and compromise. An approach needed to be taken to introduce industry standard and appropriate security controls for industrial applications.
The Solution: Identified security control gaps were addressed by a solution proposal. The environmental constraints of the factory environments necessitated the research and development of authentication workflows beyond standard authenticating factors such as email addresses or mobile devices. The newly developed security workflows were implemented into a testing environment, with security and functionality testing carried out. The security controls test solution was then transferred to SA for implementation into the production environment by the industry partner (execution is underway).
-

Automated Transformer Unicore Stacking
August 2021
Rex Power Magnetics is a Canadian dry-type transformer design and manufacturing company, headquartered in Concord, Ontario (Greater Toronto Area). In collaboration with the team at the Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing (formerly known as the Centre for Advanced Manufacturing and Design Technologies), they aimed to integrate robotics to eliminate safety risks and increase productivity.


Funding Agency/Program: FedDev Ontario/ SONAMI
Industry Partner: Rex Power Magnetics
Principle Investigators: Ramzy Ganady, Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing; Saleh Jiddawi, Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing
Student Research Assistants: Drew Pitchford (MEET), Mohamed Kasim (MEET)
Technology Areas: Robotics, Programming, Pneumatic Design, Industrial Automation
The project aim was development of an alternative process to improve productivity, to replace a process that is highly repetitive and prone to injury. This project successfully automated the stacking of u-shaped, steel laminations, to create an industrial process that was repeatable and reliable without human intervention.
The Challenge: In a single core, laminations varied widely in weight, rigidity, and length. The laminations were also extremely thin and non-rigid during movement.
The Solution: The team solved this challenge using a magnetic gripper mounted onto one of the ABB Robots. The gripper had a custom cushion pad with a slight draft angle that would bend the u-shaped laminations outward. A spreader was used to spread the laminations apart before the stacking process to improve repeatability. The end of the process stacked laminations in an upright position, rotated to a horizontal position and ejected the stack to a nearby conveyor.
-

Performance Hockey Skate Orthotics
June 2021
Guelph Orthotics specializes in treating a wide spectrum of musculoskeletal and neuromuscular ailments with the use of custom orthotics and custom-made braces.
This applied research project explored the production of a hockey skate orthotic which may improve speed.


Funding Agency/Program: FedDev Ontario/ SONAMI
Industry Partner: Guelph Orthotics Inc
Principle Investigator: Dr. John Phillips, Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing
Foot and skate position has been found to be significant in creating an efficient and powerful skating stride. Based on the natural position and alignment characteristics of feet some athletes are at either and advantage or disadvantage when it comes to their skating stride.
The Challenge: The production of a hockey skate orthotic which may improve performance.
The Solution: The production of a 3D printed prototype which can be used for real world testing by the industry partner.
-
b.jpeg?h=137&w=200&rev=356b13214ac744409152a52fdd8407b0&hash=78A3FCD5391067B9EC84380552BF9CD2)
Liquid-Liquid Extraction for Metals Removal in Mining
May 2021
Hatch Ltd. is a global, multidisciplinary engineering company with headquarters in Mississauga that provides services to a wide range of industries, including mining, mineral processing, and metals. As an innovative engineering consultancy company, they actively engage in new technology development in their core areas.


Funding Agency/Program: NSERC/ ARD
Industry Partner: Hatch Ltd.
Principle Investigators: Dr. Anita Usas Neving, CHEM and Dr. Karina Lopez, CHEM
Student Research Assistants: Catherine Giu, Kevin Theodore, Gurvinder Singh Sekhon, Charnele Andrews, Bryn Smith, and Puneet Kaur Johal, MEET and CHEM
Technology Areas: Chemical Analysis, Environmental Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechanical Design
Liquid-liquid extraction is an important process in the mining industry to remove metals from water but can also have negative environmental impact and potential hazardous effects due to the large quantity of organic solvents (e.g. an organic solvent could be kerosene). The metal recovery process can also impact cost and production efficiencies for the company.
The Challenge: To improve mixing performance and minimize separation time via a new in-line mixing process which separates and recovers the metals of a mining process.
The Solution: During the course of this 3-year, multidisciplinary project, a prototype pilot plant was developed to test and evaluate different in-line mixers by mixing the water and organic solvent in the pipeline, pushing it through a settler, and testing the recovery of the metals. The work provided valuable expertise, insight and understanding of the technology, and laid the foundation for further development of this process.
-

Geotracking Wristband for Covid-19 Quarantine Monitoring
January 2021
Dapasoft is an expert in healthcare integration and aims to provide an innovative solution to help the public adhere to COVID-19 quarantine guidelines. The Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing (formerly known as the Centre for Advanced Manufacturing and Design Technologies) and Dapasoft have embarked on a research partnership to develop a solution to monitor and ensure that a person that is supposed to be quarantined remains at their quarantine location.


Funding Agency/Program: FedDev Ontario/ SONAMI
Industry Partner: Dapasoft Inc.
Principle Investigator: Saleh Jiddawi, Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing
Co-Investigators: Somayyeh Poshtiban, Mechanical and Electrical Engineering & Technology (MEET) / Douglas Whitton (Faculty of Animation, Arts & Design (FAAD), IxD )
Student Research Assistants: Sanket Patel (MEET) Yara Kashlan (FAAD)
Technology Areas: Electronics prototyping, IoT, Interaction Design
In the rapidly evolving pandemic, this research project will use cutting-edge technology to develop a geotracking wearable wristband.
The Challenge: The main challenge addressed is that of monitoring and tracking individuals under the 14-day quarantine due to COVID-19 regulations primarily related to travel restrictions.
The Solution: Design and produce an aesthetically appealing, functional prototype(s) of the quarantine tracking wristband.
-

Prototyping an AI Self Tuning Guitar Stand
November 2020
2Unify consists of a team of engineers brought together by their passion for music. In collaboration with the team at the Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing (formerly known as the Centre for Advanced Manufacturing and Design Technologies), 2Unify aims to simplify the guitar tuning process utilizing AI and Robotics.


Funding Agency/Program: FedDev Ontario/ SONAMI
Industry Partner: 2unify
Principle Investigator: Saleh Jiddawi, Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing / Ramzy Ganady, Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing
Technology Areas: AI, Prototyping
Guitar tuning can be a time-consuming, inconvenient and stressful task — especially in larger school or music settings. In order to automate this task, a research project addressed improvement of a smart stand to ensure higher accuracy, easier assembly, and a smoother hands-free experience to guitar tuning. The goal is for next generation 2unify stands to be able to tune any stringed instrument for musicians and music institutions.
The Challenge: Barriers to product development faced by the company and addressed by this project were the cost of manufacturing, assembly time, safe transportation, cord management and smart stand mechanical motion.
The Solution: 2Unify collaborated with the Centre for Intelligent Manufacturing to develop a stable and more functional 3D prototype of the Hands-Free Guitar Tuner. The project produced five prototypes using digital design and 3D printing — each one incrementally better than the last. Each prototype focused on improving multiple aspects of the product challenges. The final prototype enables the "smart" Hands-Free Guitar Tuner to be simpler to assemble and disassemble, easier to transport, and to function with greater simplicity than the previous prototype.
